

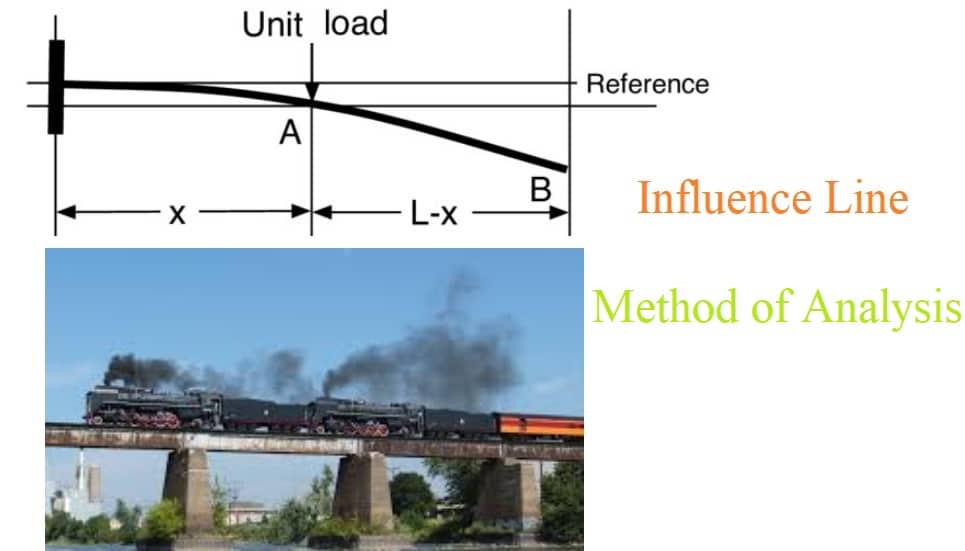
Müller-Breslau Principle for the Influence Lines for Beams Solutions: Plastic Analysis Rigid-Jointed FramesĮxample 9.1: Influence Lines for a Simply Supported Beam
Problems: Plastic Analysis Rigid-Jointed Frames Solutions: Plastic Analysis – Rigid-Jointed Frames Problems: Plastic Analysis – Rigid-Jointed Frames

Solutions: Plastic Analysis – Continuous Beams Problems: Plastic Analysis – Continuous Beams Moment Distribution for Rigid-Jointed Frames with SwayĮxample 6.2: Rolled Universal Column Section Moment Distribution for No-Sway, Rigid-Jointed Frames Unit Load Method for Singly-Redundant, Rigid-Jointed Frames Moment Distribution Method for Multi-Redundant Beams McCaulay’s Method for the Deflection of BeamsĮquivalent Uniformly Distributed Load Method for the Deflection of Beams Unit Load Method for Singly-Redundant Pin-Jointed Frames Solutions: Plastic Cross-section Properties Problems: Plastic Cross-section Properties Table of ContentsĮxample 2.1: Plastic Cross-section Properties – Section 1 As a member of the Institute of Physics, he is both a chartered engineer and a chartered physicist and has been involved in consultancy, research and teaching for more than 35 years. McKenzie is also the author of six design textbooks relating to the British Standards and the Eurocodes for structural design and one structural analysis textbook. Answer (1 of 4): An influence line diagram of a structural effect (which can be axial force, shear, bending moment, deflection, etc.) is the line that tells you what effect a unit load at some location in the structure, has at the location in the structure under analysis, including, of course, th. The x-y-z co-ordinate system and symbols have been modified to reflect the conventions adopted in the structural Eurocodes. This edition includes a rewrite of the chapter on buckling instability, expands on beams and on the use of the unit load method applied to singly redundant frames. New chapters cover the development and use of influence lines for determinate and indeterminate beams, as well as the use of approximate analyses for indeterminate pin-jointed and rigid-jointed plane-frames.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
